Battery Charge Time Calculator
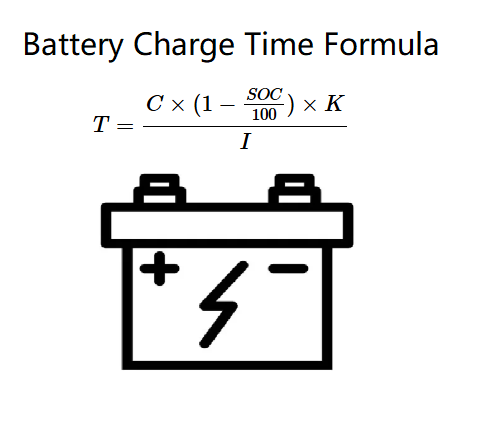
Battery Charge Time Calculation Formula
- T – Charge Time (hours)
- C – Battery Capacity (Ah)
- SOC – Current State of Charge (%)
- K – Battery Type Coefficient
- I – Charging Current (A)
Battery Charging Precautions
When charging batteries, pay attention to the following points to ensure safety, longevity, and performance:
1. Use the Right Charger
- Match Voltage and Current: Ensure the charger's output voltage and current match the battery specifications. Using an incompatible charger may cause overcharging, overheating, or damage.
- Use Original or Certified Chargers: Always use the original charger or certified third-party chargers. Avoid low-quality chargers.
2. Avoid Overcharging
- Risks of Overcharging: Prolonged charging can lead to overcharging, increasing the risk of overheating, swelling, or even explosion.
- Solution:
- Use chargers with overcharge protection.
- Avoid charging overnight or unattended for long periods.
3. Avoid Deep Discharge
- Hazards of Deep Discharge: Fully draining the battery may damage its chemical structure, reducing its lifespan and performance.
- Solution:
- Recharge the battery when it drops below 20%.
- Avoid storing the battery in a fully discharged state.
4. Control Charging Temperature
- High-Temperature Risks: High temperatures accelerate battery aging and may cause safety hazards (e.g., fire or explosion).
- Solution:
- Avoid charging in high-temperature environments (e.g., direct sunlight or near heat sources).
- If the device overheats, pause charging and let it cool down before resuming.
5. Limit Fast Charging
- Impact of Fast Charging: While convenient, fast charging can accelerate battery aging.
- Solution:
- Use standard charging modes when possible.
- Choose devices with smart charging speed adjustment.
6. Charge Regularly
- Long-Term Storage: If the battery is not used for a long time, store it at around 50% charge.
- Maintenance: Perform a full charge-discharge cycle every few months to maintain battery health.
7. Avoid Mixing Batteries
- Risks of Mixing: Using batteries of different brands, models, or conditions may lead to uneven charging and reduced lifespan.
- Solution:
- Use batteries of the same brand, model, and condition.
- Replace all batteries at the same time when needed.
8. Monitor Battery Aging
- Signs of Aging: Reduced capacity, longer charging times, and excessive heat.
- Solution:
- Regularly check battery health and replace it if necessary.
- Avoid using significantly aged batteries to prevent safety risks.
9. Prevent Physical Damage
- Damage Risks: Squeezing, puncturing, or dropping the battery may cause internal short circuits, leading to hazards.
- Solution:
- Handle batteries gently and avoid physical impacts.
- Use protective cases or covers.
10. Understand Battery Types
- Charging Characteristics:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Avoid overcharging and deep discharging. Prefer shallow charging cycles.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: Fully discharge before charging to avoid memory effect.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Avoid deep discharge and perform regular equalization charging.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back