Ups Battery Size Calculator
Ups Battery Size Calculation Explanation
Based on the principle of energy conservation, the formula is as follows:
- C – Battery Capacity (Ah)
- PL – UPS Output Power (W or kW, selectable)
- T – Backup Time (h, min, or s, selectable)
- Vbat – Battery Voltage (V)
- η – UPS Efficiency (0.90-0.95, depending on model)
- K – Battery Discharge Efficiency (refer to table values)
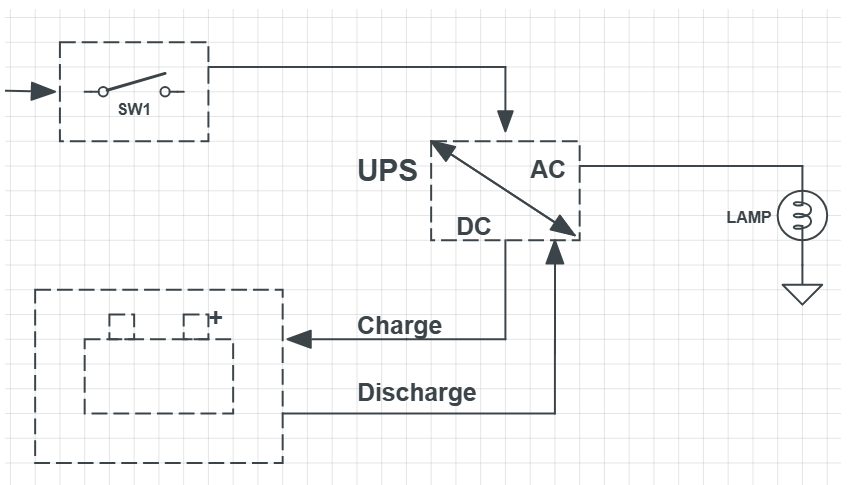
What is a UPS?
UPS stands for Uninterruptible Power System or Uninterruptible Power Supply.
It consists of a battery connected to the main unit and a circuit module, including an inverter that
converts DC power into AC power.
The primary purpose of a UPS is to provide a stable and uninterrupted power supply to devices, such as
computers, network systems, or electronic equipment like solenoid valves and pressure transmitters.
-
During normal power conditions: The UPS stabilizes the main power supply and provides it to connected devices, functioning as an AC voltage stabilizer while charging its internal battery.
-
In case of power failure: The UPS immediately switches to the stored DC energy in its battery, converting it into 220V AC power via the inverter. This ensures uninterrupted power to the load and protects connected devices from damage.
What is a Lithium-Ion Battery?
A lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery that uses lithium metal or lithium alloy as the negative electrode material and a non-aqueous electrolyte solution.
There are two main types of lithium-ion batteries:
- Lithium metal batteries: Contain metallic lithium and are generally non-rechargeable.
- Lithium-ion batteries: Do not contain metallic lithium and are rechargeable.
What is a Lead-Acid Battery?
A lead-acid battery is a type of battery where the electrodes are primarily made of lead and lead dioxide, with sulfuric acid as the electrolyte.
- During discharge: The positive electrode primarily consists of lead dioxide, and the negative electrode is lead.
- During charging: Both electrodes primarily consist of lead sulfate.
Comparison Between Lithium-Ion and Lead-Acid Batteries
-
Operating Temperature Range:
- Lithium-ion batteries: Operate between -20°C to 60°C, reducing installation and maintenance costs.
- Lead-acid batteries: Operate within a narrower range of 15°C to 35°C.
-
Environmental Impact:
- Lithium-ion batteries: Free of harmful heavy metals, making them environmentally friendly.
- Lead-acid batteries: Contain heavy metals like lead and antimony, which can cause significant environmental pollution if not disposed of properly.
-
Discharge Characteristics:
- Lithium-ion batteries: Offer stable discharge performance under varying loads and temperatures.
- Lead-acid batteries: Display significant fluctuations in discharge performance, leading to inconsistent power delivery.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back